How is the vagus nerve linked to diseases and disorders?
The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system activities balance each other to maintain homeostasis (Bonaz, Sinniger and Pellissier, 2017). If this balance is disrupted it results in the development of various pathologies.
Inflammation may be a local or temporary event and, once treated/resolved, the immune and physiological homeostasis is restored. However, disrupted innate immune regulation can result in continual pro-inflammatory cytokine activity and excessive or chronic inflammation. This state underlies the pathogenesis of a range of disease syndromes and autoimmune disorders (Pavlov and Tracey, 2012).
The vagus nerve is a major constituent of a neural reflex mechanism — the inflammatory reflex — that controls innate immune and inflammatory responses during illness and tissue injury.
The inflammatory reflex is a centrally integrated physiological mechanism in which afferent vagus nerve signaling, activated by cytokines or pathogens, is functionally associated with efferent vagus nerve-mediated output to regulate pro-inflammatory cytokine production and inflammation.
The absence of the inflammatory reflex results in excessive innate immune responses and cytokine toxicity (Pavlov and Tracey, 2012).
Figure 1: Inflammatory reflex anatomy.
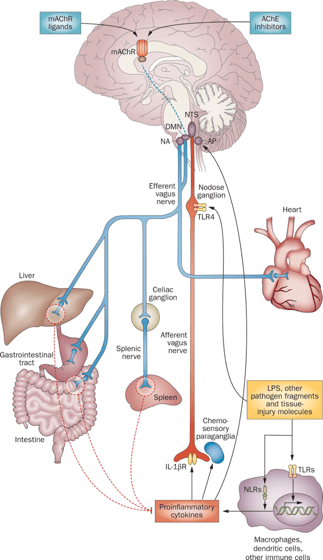
Inflammatory mediators (cytokines) are released by macrophages when toll-like receptors (TLRs) and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors (NLRs) are activated.
These mediators are detected by sensory components of the afferent arm of the inflammatory reflex (red). Neuronal interconnections between the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS), area postrema (AP), dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve (DMN), and nucleus ambiguus (NA), and integrate afferent signaling and efferent vagus nerve-mediated immunoregulatory output.
The efferent vagus nerve cholinergic output to the spleen, liver and gastrointestinal tract (blue) regulates immune activation and suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokine release (dotted red lines).
This arm of the inflammatory reflex can be activated in the brain through muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (mAChR) - mediated mechanisms triggered by mAChR ligands and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors (Pavlov and Tracey, 2012).
The Byond Healthcare knowledge hub is exists to share expert content about the vagus nerve and the benefits of vagus nerve stimulation, with a specific focus on non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation, with patients, healthcare providers and medical representatives.